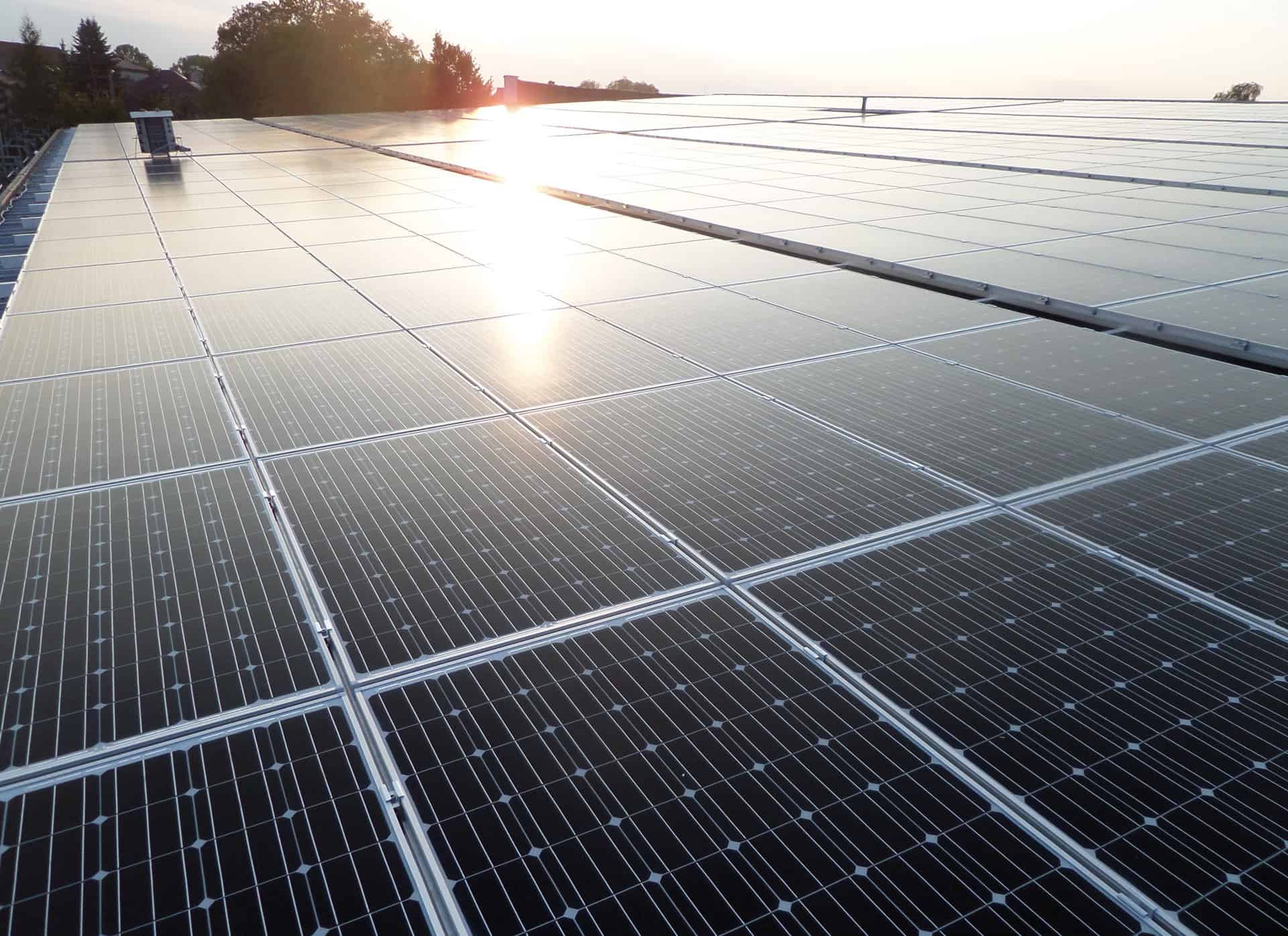
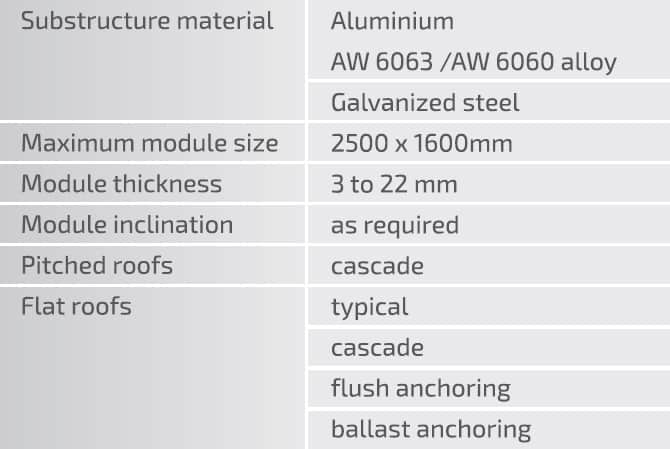
Currently photovoltaic roof systems are the most popular and widely available solutions in the BIPV market; however, they are not always the right or most feasible choices. When designing roof-mounted PV modules, the criteria of wind resistance (and detachment by wind) become of utmost importance, along with the verification of roofing load capacity; more often than not, the roofing structure cannot withstand any loads larger than for which they were originally designed. Unfortunately, PV system installers disregard these factors all too often, and this may lead to a building disaster. With this risk in mind, ML System provides PV modules with standardised substructure systems the strength of which is adequate to the actual external loads. The PV modules can be installed on roofs by flush anchoring or ballast anchoring.
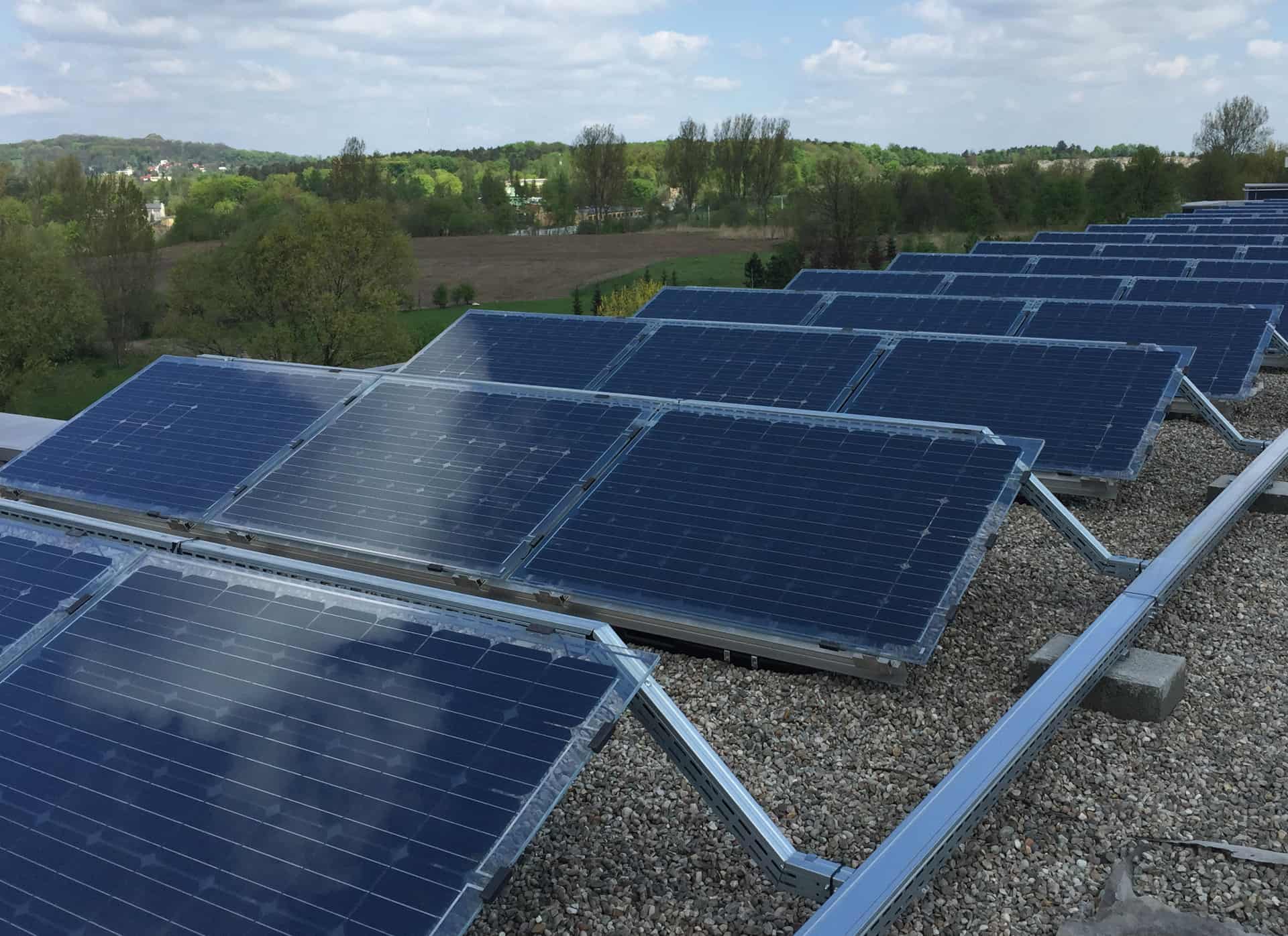
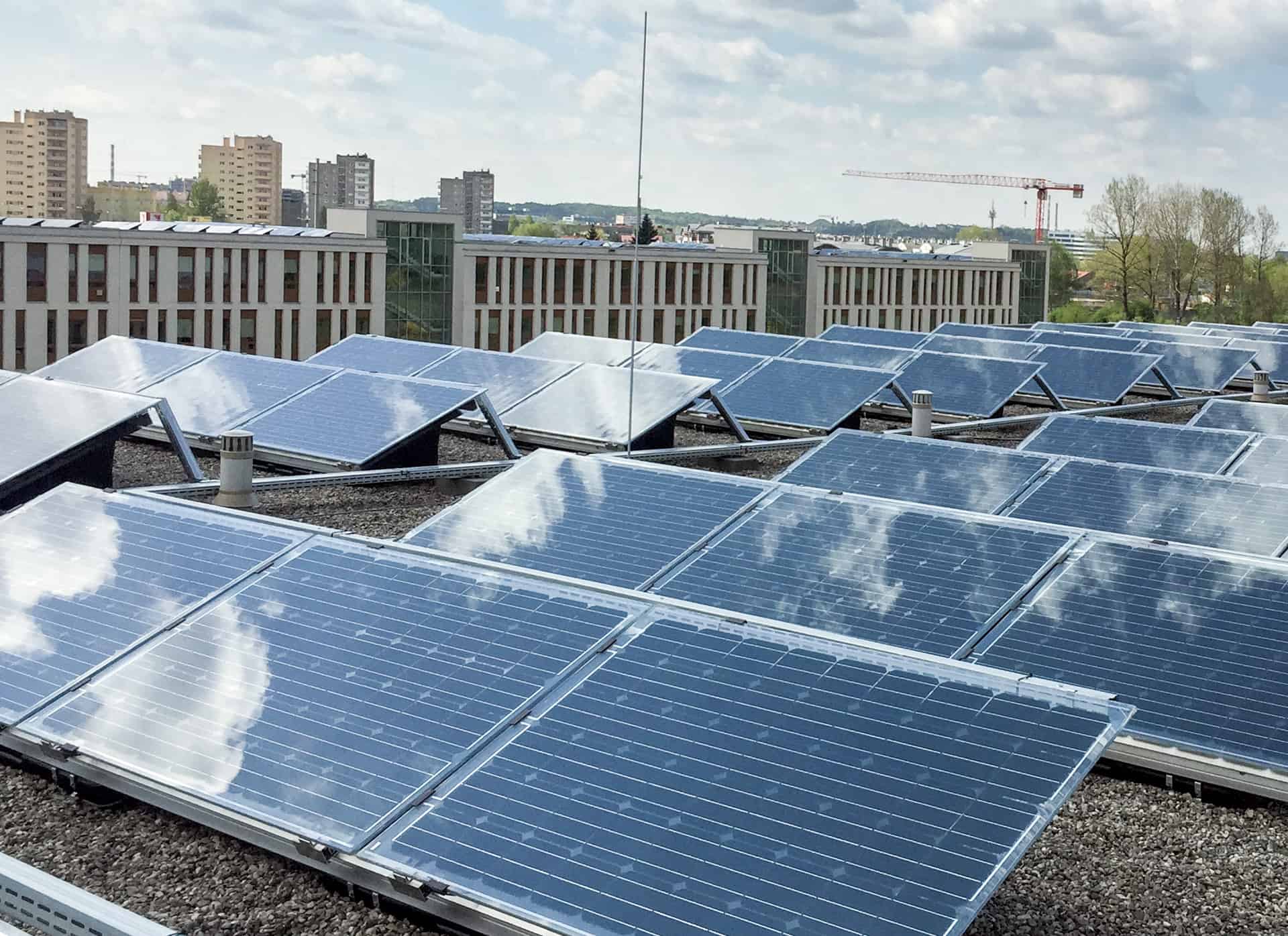
High roof slopes require flush anchoring. The flush anchoring system features fasteners which penetrate the roofing layers; thanks to the specially provided sealing accessories, these penetrations remain watertight. Flat or low incline rooftops can have the PV modules anchored by ballasting. Ballast anchoring eliminates the need to puncture the roof slope; the downside is the extra weight of the PV modules. PV modules installed on flat roofs can be aligned to the south or in an east to west orientation.
The flat rooftop aluminium substructure system comprises lengthwise mounting rails, lightweight triangular stands, and stainless hardware and accessories.
The aluminium grid work can be anchored directly with concrete blocks. This mounting system prevents piercing the roofing insulation layers and keeps the PV installation impervious to gusts of wind.
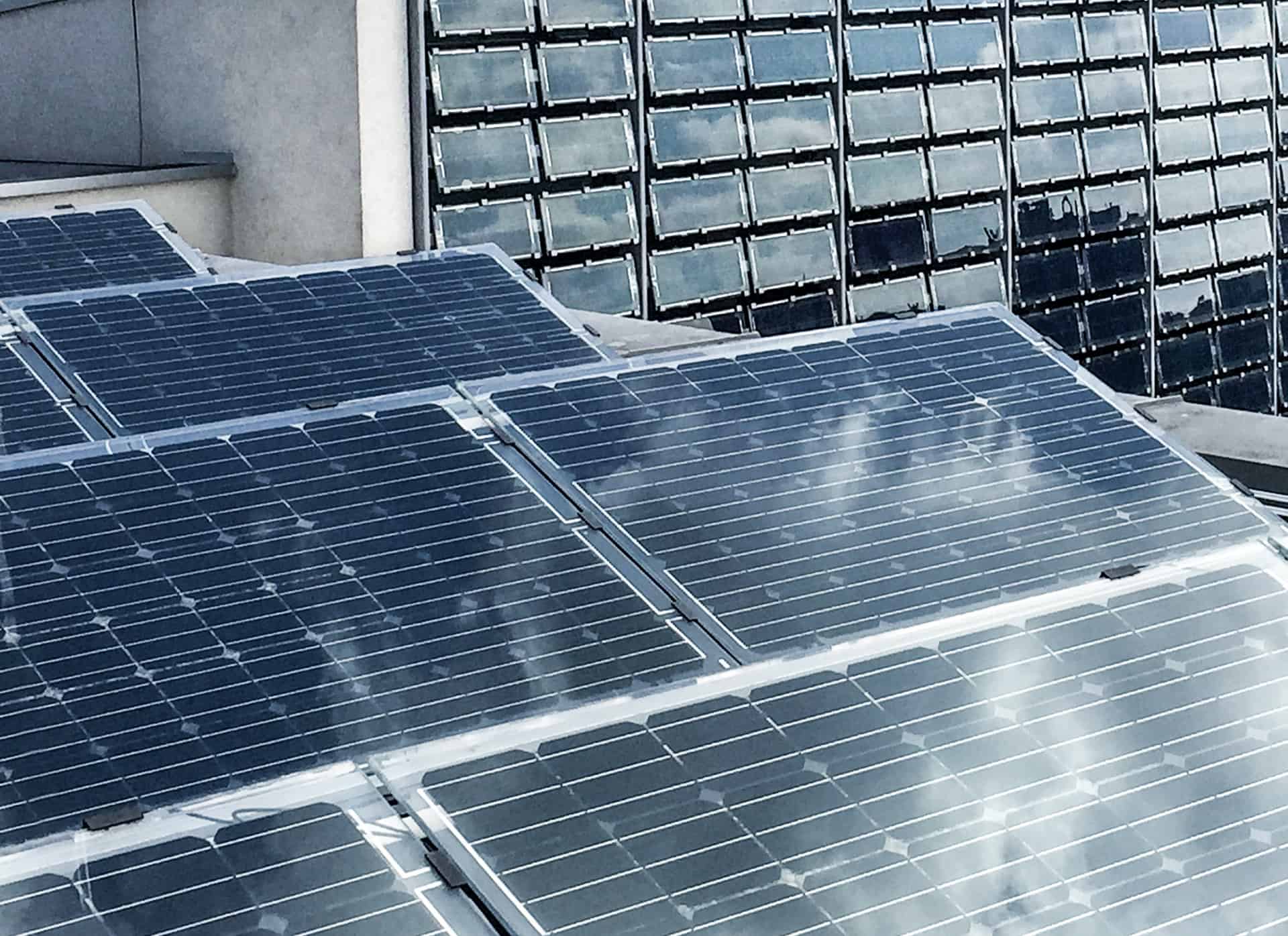
Another roof installation mounting variant for the PV modules is the cascade system. It can be applied on virtually all roof types: high-pitch roofs, where it runs in parallel to the slope, or on flat roofs, where a substructure is installed to provide a higher slope. In each case, the cascade system allows the free drainage of water and the sliding of snow. This also prevents the deposition of dirt.
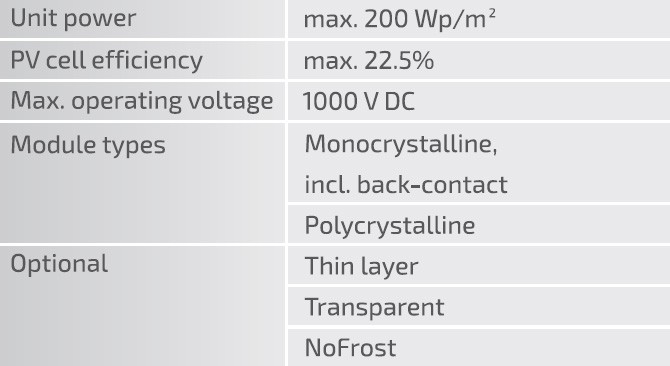
Combining the cascade system with the NoFrost system will dispense with the need to clear the snow from the PV modules. Aligning the modules in a single plane will eliminate cross-shading and prevent snow piling up between the individual rows of PV modules. The solution uses no-frame glass-to-glass PV modules, in the opaque or transparent version. Aside from the technical value, the system is very aesthetic in appearance and facilitates the application of photovoltaic power sources to monumental structures (e.g. transparent PV modules with coloured PV cells on a substructure in a colour to match the roofing). PV modules are available in irregular shapes (triangular and diamond, for roof edges and ridges) to adapt the PV module array to the roof form.